Dead or dormant? How to tell if your plants survived Texas’ winter blast
Last week Central Texans watched as snow and ice blanketed landscapes in a series of storms rivaling Northern blizzards.
As power is restored, water becomes safe to drink and the process of repairing damage has begun, it’s time for garden assessment.
It’s ugly out there. Finally able to walk my dogs, I found downed tree limbs or cut brush at almost every house in our neighborhood. Prized agaves, sago palms and other specimen plants turned to rotting mush. Tough-as-nails rosemary bushes sport black branches. This unprecedented freeze damage has left even seasoned gardeners wondering what will return and what’s gone for good? Is it dead or is it dormant?
We normally only have a few weeks left until the danger of frost has passed. According to the USDA Hardiness Zone map for the Austin area, our average last frost occurs between March 1 and March 31. It’s usually the middle of March. But it hasn’t been a typical winter.
The most important thing right now is to wait. If you prune a dormant plant right now and warm weather stimulates growth, the new leaves will be highly susceptible if we have another freeze, and it will then die. If you wait until the danger of frost has passed, you will give your dormant plants a fighting chance.
Palm trees
Native Sabal minor palm trees tolerate freezes in most years. Most other palms won’t make it. If the center bud is firm, the plant might survive. Cut off drooping, dead or damaged leaves. If your palm has a rotting crown, or you can easily pull fronds out of the trunk, it won’t come back. If you’re unsure, however, give it plenty of time to recuperate.
Cycads – Sago palms
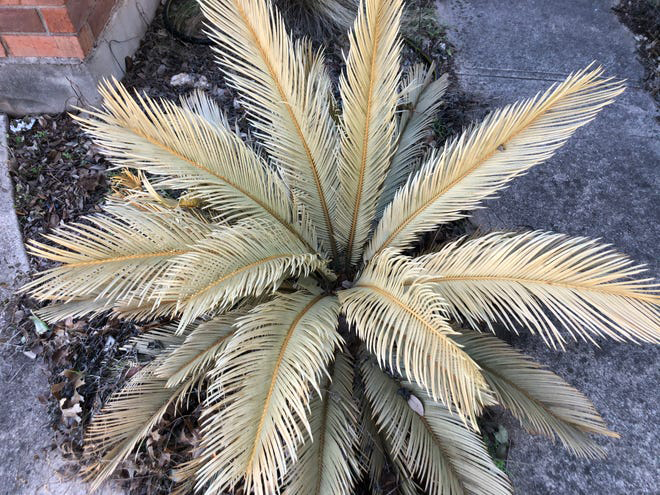
Many Austin gardeners enjoy the drama of large Sago palms in their landscapes. Not actually palms, Sagos are cycads. They generally tolerate temperatures down to 15 degrees. Frost-damaged leaves turn yellow or brown and should be removed. If the trunk and leaf crown are hard wood, it should recover. If the trunk turns soft, your sago might be damaged beyond recovery. After the freeze of 2010, Sagos across town were devastated but most had no crown damage. By summer, new leaves emerged and the plants thrived.
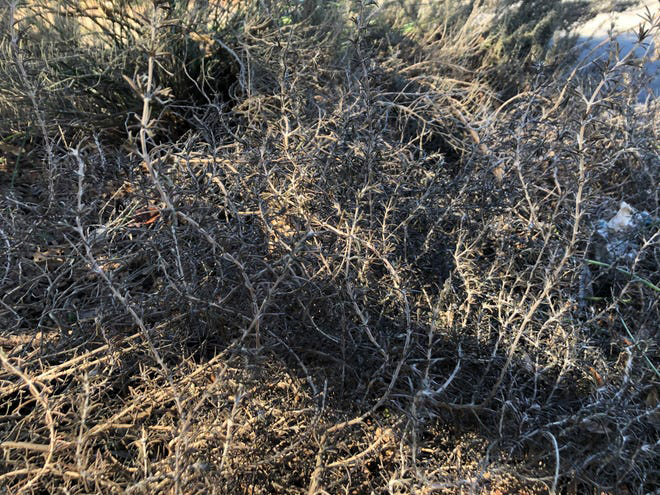

This rosemary has survived 20-plus years, but not the winter storm of 2021. It probably won’t come back.
Shrubs and woody perennials
Rosemary normally does fine in our mild winters, even handling a few light frosts for short periods. Days on end of single-digit weather and wet snow spelled the end of the road for even the most established plants. You can remove them at any time — they won’t be coming back.
Salvias range from cold hardy to tender. Some Salvia Greggiis even survive to 0 degrees. If you don’t know your exact variety, the best approach is to cut them back to green wood. Once you see green inside the cut, stop. If you don’t see any green, simply cut it back to the ground and be very patient. It may come back from the roots, given a few months.
Take the same approach with shrubs and other woody perennials that appear dead like pittosporum, loropetalum, lantana and boxwood.
Succulents
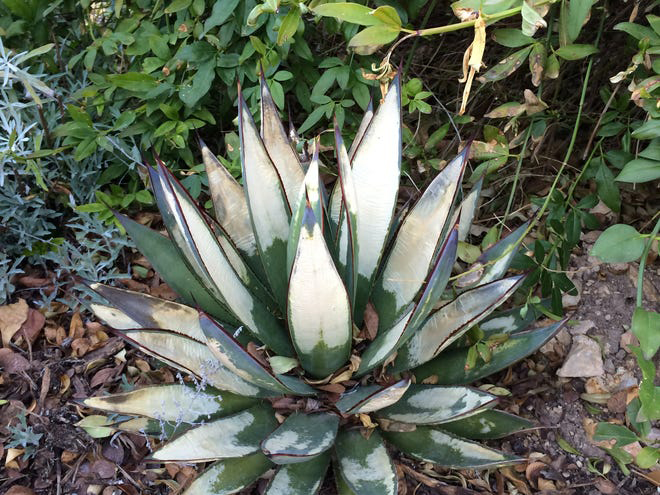
We know some plants simply aren’t cold hardy. Many agaves, cacti and other succulents won’t survive after the prolonged deep freeze and snow. A handful of species might have weathered the storm, and you’ll know if there is hope if you have a firm center inside the collapsed outer leaves.
Sotols, Yuccas and Nolinas are usually Texas tough. Many in my garden and elsewhere are looking great after the winter assault. Whale’s tongue and havardiana agaves are reported to have survived in some landscapes as well.
Cacti
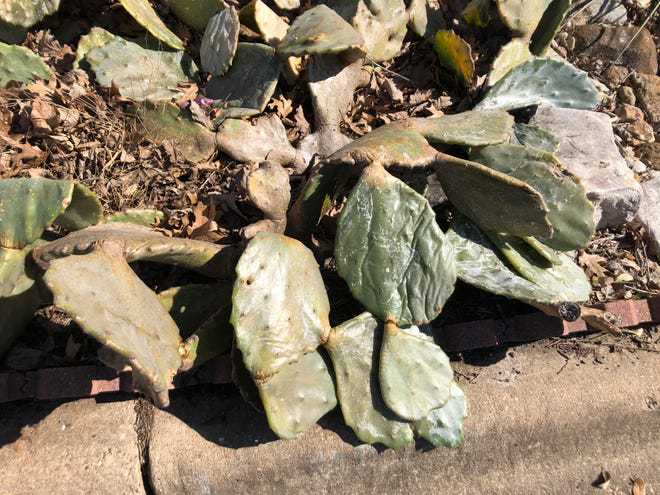
Crumbled mounds of mush, prickly pear cacti simply disintegrated all over town. There might be hope for some of them, however, depending on the species. Some varieties of Optunia are hardy to 15, 10 or 0 degrees.
Cacti are very sensitive to the timing of pruning. While their dying pads and stems look terrible, it is important to wait until it is really warm to prune them. Then dust the big cuts with sulfur to help dry out the cuts. Jointed cacti regenerate really well, but the columnar ones should be cut back to the base or you will just end up with a permanent stump. If the plant is oozing, you can remove it now.
Our plants took an incredible hit. Those that survive will need much longer to recover than milder years.
Once, after a terrible freeze, I advised my clients repeatedly to wait longer before pulling out plants. I ignored my own advice and ripped out a very small Anacacho Orchid Tree only to find the tiniest green growth at the base of the plant that was hidden by mulch. So, wait, wait, and wait some more.










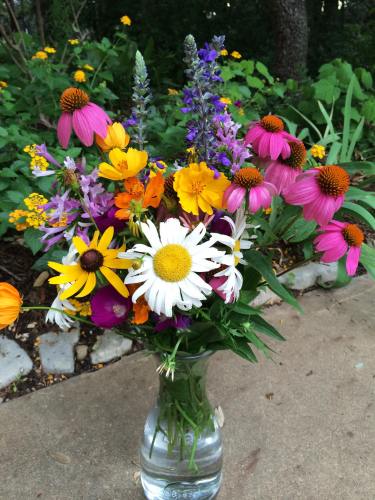

 Almost anything in your garden can be worked into a bouquet. Now that you’ve identified some of your own pretty garden flowers that you’d like to put into a vase, how do you start?
Almost anything in your garden can be worked into a bouquet. Now that you’ve identified some of your own pretty garden flowers that you’d like to put into a vase, how do you start?
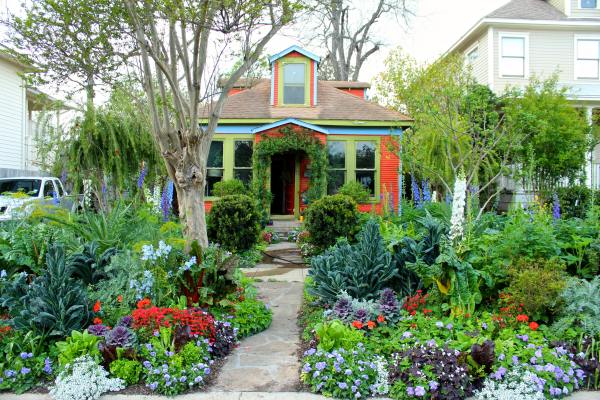
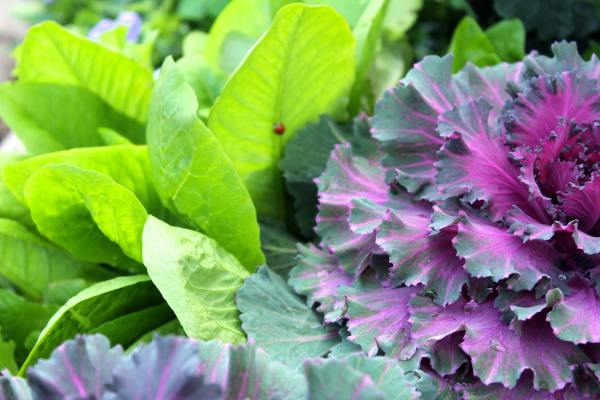
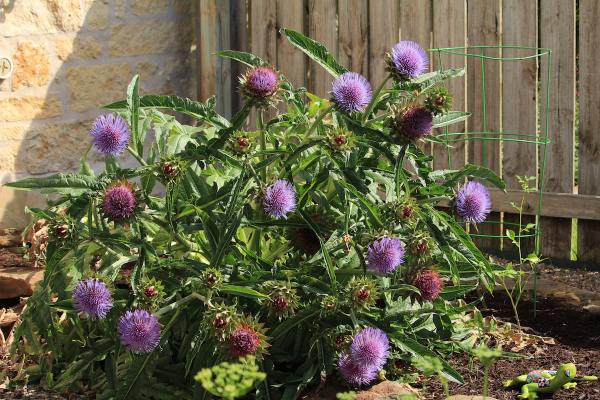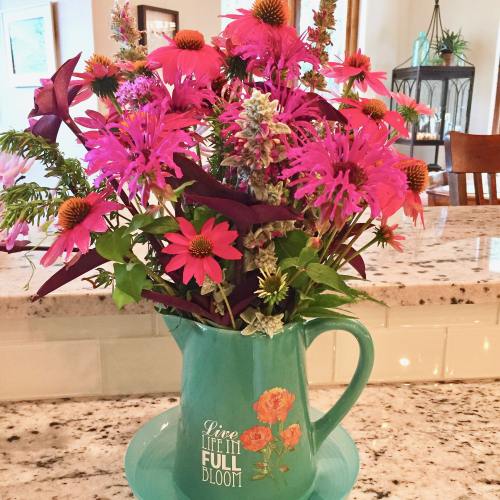


 Many edibles also provide interesting contrast by adding unique texture and form into the mix. Artichokes, with their large, spiky leaves and brilliant lavender thistle-like blooms make stunning sculptural focal points. Thick-veined and curly greens stand out when planted next to smaller, softer border plants like zexmenia, purple skullcap or damianita. Feathery dill plants give the garden a wispy element to include next to woody perennials.
Many edibles also provide interesting contrast by adding unique texture and form into the mix. Artichokes, with their large, spiky leaves and brilliant lavender thistle-like blooms make stunning sculptural focal points. Thick-veined and curly greens stand out when planted next to smaller, softer border plants like zexmenia, purple skullcap or damianita. Feathery dill plants give the garden a wispy element to include next to woody perennials. There’s a lot going on right now, and I’m sure you’re looking for some stress relief, escape, and distraction. Luckily, you only need to look as far as your yard for a place to meditate, exercise, and get your hands in some healing dirt. Studies demonstrate that spending time in a garden can improve our well-being – both physically and mentally.
There’s a lot going on right now, and I’m sure you’re looking for some stress relief, escape, and distraction. Luckily, you only need to look as far as your yard for a place to meditate, exercise, and get your hands in some healing dirt. Studies demonstrate that spending time in a garden can improve our well-being – both physically and mentally. Design your own garden workout routine at home. Gardening chores are excellent exercises and offer anything from soothing stretches to serious cardio. Did you know raking leaves for 30 minutes burns 225 calories – and provides weight training and tones all the major muscles groups in your body. Choose your chore, from raking, pruning, digging or hauling bags of mulch.
Design your own garden workout routine at home. Gardening chores are excellent exercises and offer anything from soothing stretches to serious cardio. Did you know raking leaves for 30 minutes burns 225 calories – and provides weight training and tones all the major muscles groups in your body. Choose your chore, from raking, pruning, digging or hauling bags of mulch. Make a plate and eat your lunch outside and listen to the birds.
Make a plate and eat your lunch outside and listen to the birds.
 Plants grow, and some of them grow a lot once they’re out of that tiny pot you bought and nestled in your lovely garden. Planting too close together creates more work later as you struggle to prune all the time or are forced to remove plants to allow enough space for them all to thrive. Believe nursery tags and nursery staff and follow the guidelines in your research.
Plants grow, and some of them grow a lot once they’re out of that tiny pot you bought and nestled in your lovely garden. Planting too close together creates more work later as you struggle to prune all the time or are forced to remove plants to allow enough space for them all to thrive. Believe nursery tags and nursery staff and follow the guidelines in your research. The plants in the front of your layered beds will be ground covers or border plants. For most gardens, these plants typically don’t get much bigger than about 18” tall. There are, of course, exceptions, depending on the overall scope and proportion of the landscape, whether it’s a very small space or a sizeable piece of property. The true test is how they will look in comparison to the next line or area of plants behind them in the bed. Border plants should provide a contrast in size between layers and should look good together, combining different colors, textures and shapes.
The plants in the front of your layered beds will be ground covers or border plants. For most gardens, these plants typically don’t get much bigger than about 18” tall. There are, of course, exceptions, depending on the overall scope and proportion of the landscape, whether it’s a very small space or a sizeable piece of property. The true test is how they will look in comparison to the next line or area of plants behind them in the bed. Border plants should provide a contrast in size between layers and should look good together, combining different colors, textures and shapes. The terms full sun, full shade, part sun, part shade are associated with specific amounts. Full sun means a site gets at least 6 full hours of sun most days. But, here in Central Texas, some plants labeled full sun may still struggle if that’s all blistering afternoon sun. Do your research to determine if there are any limits on tolerance that might apply.
The terms full sun, full shade, part sun, part shade are associated with specific amounts. Full sun means a site gets at least 6 full hours of sun most days. But, here in Central Texas, some plants labeled full sun may still struggle if that’s all blistering afternoon sun. Do your research to determine if there are any limits on tolerance that might apply. Full shade doesn’t mean no sun at all. Labels calling for full shade conditions refer to less than 3 hours of sunlight each day, and filtered light the remainder of the day. In the Austin area, those 3 hours simply cannot fully expose plants in the heat of the day. A little dappled morning light and good afternoon shade is a much better guide for us.
Full shade doesn’t mean no sun at all. Labels calling for full shade conditions refer to less than 3 hours of sunlight each day, and filtered light the remainder of the day. In the Austin area, those 3 hours simply cannot fully expose plants in the heat of the day. A little dappled morning light and good afternoon shade is a much better guide for us. Border plants don’t have to be planted in a straight line. You can also cluster plants in sections according to size, color or texture. Place them in drifts in front of the next section of larger plants based on which ones look best together.
Border plants don’t have to be planted in a straight line. You can also cluster plants in sections according to size, color or texture. Place them in drifts in front of the next section of larger plants based on which ones look best together. Many annuals also make excellent border plants, adding color and interest at specific times through the year and allowing you to change out your look with the seasons.
Many annuals also make excellent border plants, adding color and interest at specific times through the year and allowing you to change out your look with the seasons.